
Grehlin and Leptin are hormones that have a significant role in energy balance and body weight regulation.
Leptin, primarily secreted by adipocytes (fat cells), is known as the “satiety hormone” as it helps to regulate energy balance by inhibiting hunger.
Leptin communicates with the hypothalamus in the brain, signaling the body has had enough to eat.
It plays a key role in maintaining body weight because, as fat mass decreases, the level of plasma leptin falls, stimulating appetite and suppressing energy expenditure until the fat mass is recovered.
Conversely, as fat mass increases, the level of plasma leptin increases, suppressing appetite until weight is lost.
If this feedback mechanism fails, it could lead to obesity.
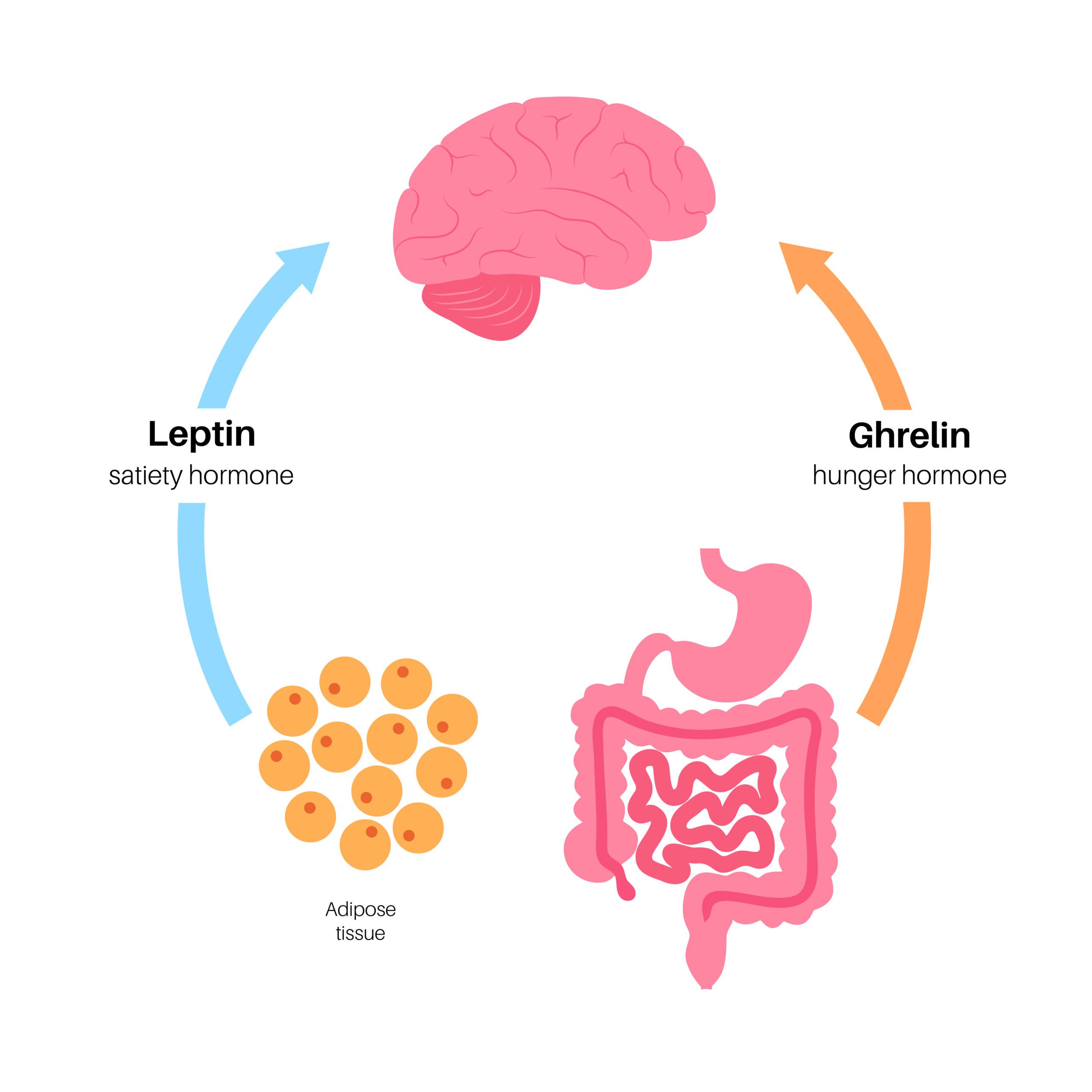
On the other hand, ghrelin is often dubbed the “hunger hormone“.
It is produced and released primarily by the stomach.
Ghrelin has numerous functions.
It stimulates the brain, which leads to an increase in appetite, and it slows metabolism and reduces the body’s ability to burn fat.
Ghrelin’s role in weight management is the polar opposite of leptin’s.
When the stomach is empty, ghrelin is secreted. When the stomach is stretched, secretion stops.
It acts on hypothalamic brain cells both to increase hunger and to increase gastric acid secretion and gastrointestinal motility to prepare the body for food intake.
The balance between these two hormones is crucial in maintaining a healthy weight.
The disruption of the delicate balance, where there’s resistance to the effects of leptin or an overproduction of ghrelin, can lead to overeating and weight gain, ultimately contributing to obesity.
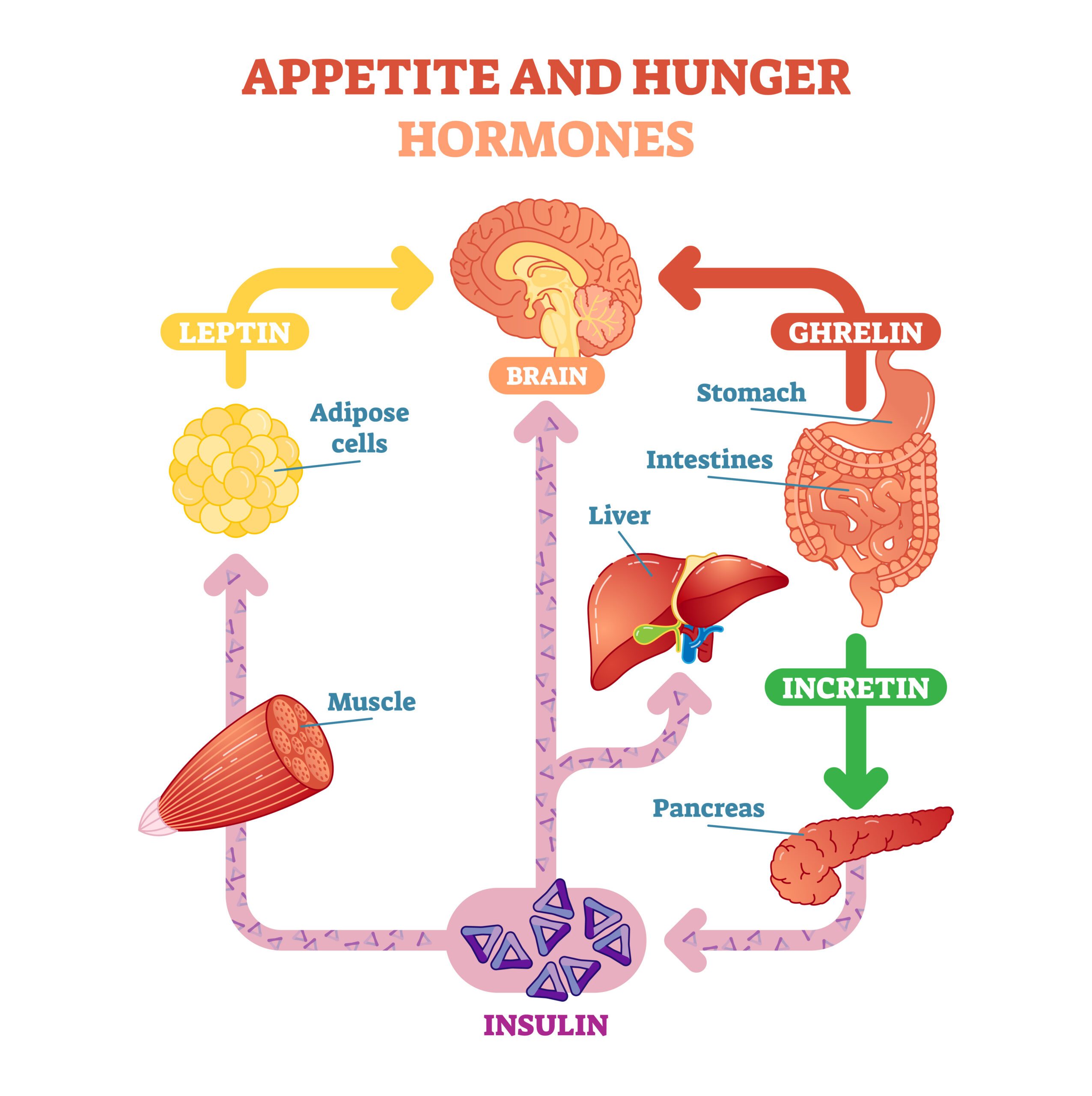
In healthy individuals, these hormones work like a checks-and-balances system for body weight:
Ghrelin rises before meals to stimulate appetite and falls after meals, while leptin rises after meals to promote satiety and suppress appetite.
Researchers studying these hormones have made significant strides in understanding the biology of weight control and obesity.
Future therapies aimed at weight loss could involve strategies that modulate these hormones to restore balance.
However, as of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, there’s still a lot to learn about how these hormones work and how they can be harnessed to treat obesity and other metabolic disorders.

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]