How Muscle Mass Affects Aging: The Key to Vitality and Longevity
August 4, 2024
 467
467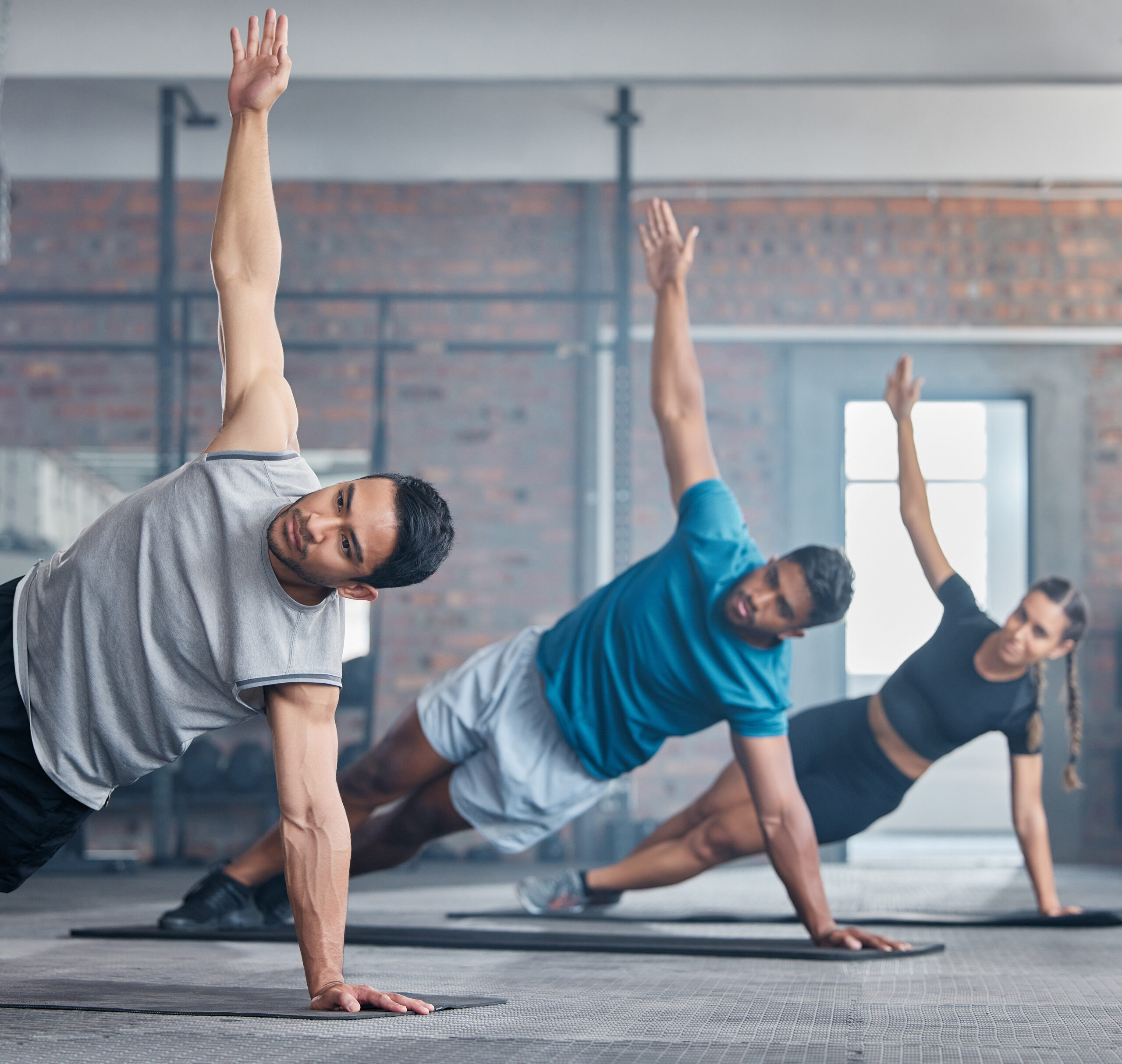 
Maintaining muscle mass as we age is crucial for vitality and longevity. The natural decline in muscle mass, known as sarcopenia, can lead to numerous health issues, including reduced mobility, increased risk of falls, and higher mortality rates. However, with proper lifestyle interventions, it is possible to mitigate these effects and maintain a higher quality of life.
Sarcopenia is the age-related loss of muscle mass, strength, and function. This process typically begins around the age of 30 and accelerates after the age of 60. The decline in muscle mass is associated with several factors, including reduced physical activity, hormonal changes, and inadequate nutrition.
Muscle mass plays a critical role in overall health and longevity. Here are some key impacts:
Maintaining muscle mass as we age requires a combination of exercise, nutrition, and lifestyle modifications.
Muscle mass is a key determinant of vitality and longevity. By engaging in regular resistance training, maintaining a balanced diet rich in protein, and leading an active lifestyle, older adults can significantly slow down the progression of sarcopenia and improve their quality of life. The message is clear: use it or lose it. Investing in muscle health today can lead to a longer, healthier, and more independent life.Maintaining muscle mass is not just about physical strength; it is about preserving the ability to live life to the fullest as we age.
Incorporating specific foods and supplements into your diet can help preserve lean muscle tissue, especially as you age. Here are five effective options:
Whey protein supplements are highly effective for muscle maintenance. They provide all essential amino acids and are quickly absorbed by the body, making them ideal post-workout. Whey protein isolate is particularly beneficial as it is low in fat and carbohydrates.
Creatine is one of the most researched supplements for muscle growth. It helps increase muscle mass, strength, and exercise performance. It also aids in muscle recovery and can be particularly beneficial for older adults when combined with resistance training.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help preserve muscle mass. They are also linked to improved muscle protein synthesis and reduced muscle loss in older adults.
BCAAs, including leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are essential for muscle protein synthesis and can help reduce muscle soreness and fatigue. They are particularly useful during periods of caloric restriction or intense training. Incorporating these foods and supplements into your diet, along with regular resistance training, can significantly help in preserving lean muscle tissue and supporting overall muscle health.
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/muscle-building-foods
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/26-muscle-building-foods
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/supplements-for-muscle-gain
https://www.bodybuilding.com/content/fat-loss-muscle-gain-supplement-guide.html
https://www.nia.nih.gov/news/how-can-strength-training-build-healthier-bodies-we-age
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2804956/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4035379/
https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/preserve-your-muscle-mass
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-38893-0
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23167-sarcopenia
Stop The Clock: The Shocking Truth About Age-Related Muscle Loss and Steps to Fight Back
Enjoy Stronger Muscles, Higher Vitality, and a Longer, Healthier Life

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]