Meat Glue Exposed: The Hidden Hazard in Processed Meats
July 22, 2024
 557
557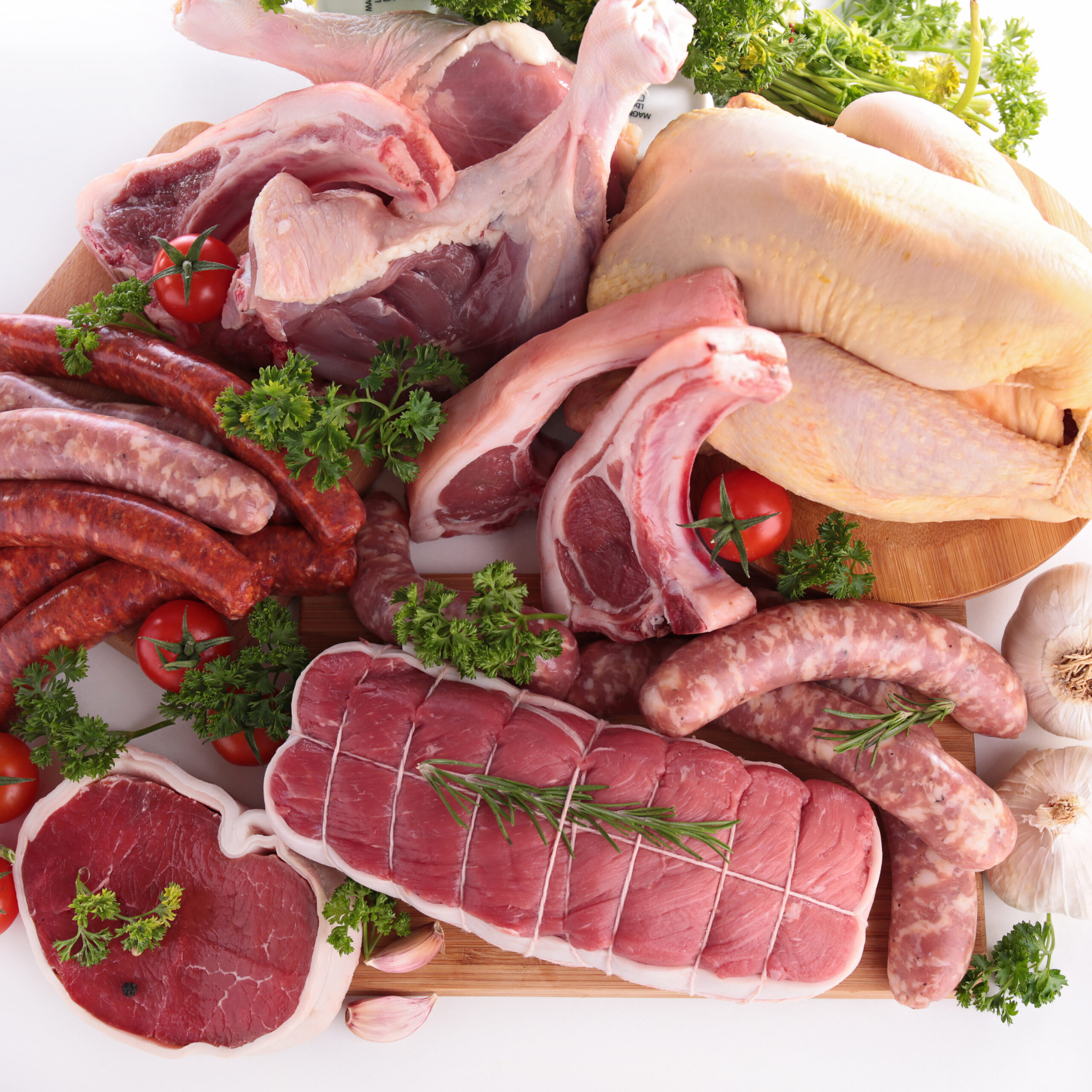 
Did you know that there lurks an invisible ingredient in meat that has been raising health concerns —It is called meat glue- scientifically known as transglutaminase?
Transglutaminase is an enzyme used to bind pieces of meat together to create larger, more uniform cuts that create a seamless appearance. Understanding such ingredients is essential for maintaining a healthy Diet and Fitness regimen, as it helps consumers make informed choices about the quality and safety of the foods they eat.
According to the American Meat Institute, it is estimated that around 8 million pounds of meat were glued in the USA in 2011, and it is likely that this number has increased over time.
While this practice may seem harmless, the hidden dangers of meat glue extend far beyond mere culinary trickery. From potential allergenic reactions to bacterial contamination, the risks associated with this additive warrant a closer examination.
Join us as we delve into the world of meat glue, uncovering the truths that every health-conscious individual needs to know.
Meat glue is used in a variety of products including ham, chicken, fish, pizza toppings, sausages, hot dogs, and even some dairy products like cheese and yogurt. Plus the use of meat glue goes well beyond meat products. It’s used in various food processing applications, including dairy products, baked goods, and plant-based proteins, to improve texture, appearance, and functional properties.
Where does meat glue come from?
The most widely used commercial transglutaminase today is the microbial version produced through bacterial fermentation. This enzyme is calcium-independent, unlike some mammalian transglutaminases that require calcium.
Based on the search results, meat glue (transglutaminase) poses several potential dangers to consumers:
It’s important to note that while transglutaminase is considered “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS) by the FDA, these potential risks have led some experts and consumers to call for more thorough safety evaluations and stricter regulations on its use in food products. As awareness of such ingredients grows, it becomes increasingly important to focus on healthy foods to eat that prioritize safety and nutritional value, allowing consumers to make informed decisions about their dietary choices.
To avoid meat glue (transglutaminase) in your food, here are some key strategies:
Remember, while transglutaminase is considered safe by the FDA, some consumers prefer to avoid it due to concerns about food quality and potential bacterial risks. Being vigilant and informed is key to avoiding meat glue if that’s your preference. Many Healthy Lifestyle Blogs emphasize the importance of understanding food ingredients and making informed choices, helping individuals align their diets with their health values and preferences.
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/transglutaminase
https://www.webmd.com/diet/is-transglutaminase-safe
https://www.yimingbiotechnology.com/meat-enzymes/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21415882/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3971462/
https://www.webmd.com/diet/is-transglutaminase-safe
https://foodinsight.org/what-is-transglutaminase/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3971462/
https://www.yimingbiotechnology.com/what-is-transglutaminase-and-is-it-edible.html
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/transglutaminase
https://www.webmd.com/diet/is-transglutaminase-safe
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8537092/
https://nutritionfacts.org/video/is-meat-glue-safe/

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]