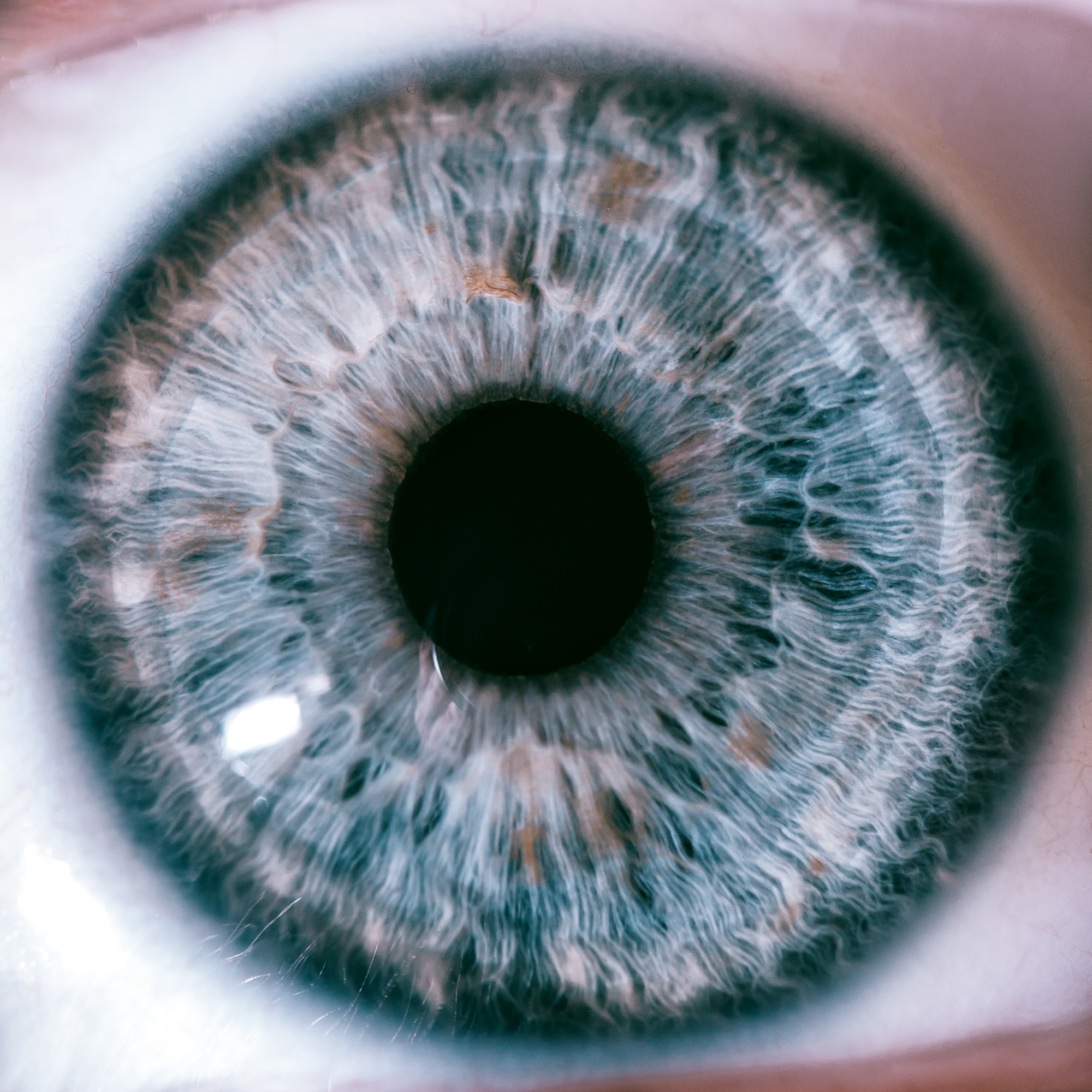
If your days are spent in front of a computer screen or working outside in the glaring sun, then tired and irritated eyes may be a daily problem for you. Luckily, there is a super nutrient that can come to the rescue. It’s an antioxidant called astaxanthin and can give you much needed relief from the symptoms often associated with eyestrain.
What is astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid. Carotenoids are naturally occurring pigments with robust antioxidant properties. Astaxanthin is commonly found in marine and aquatic animals such as salmon, which explains the characteristic pink color. Chances are you’re not getting all you need from your diet alone.
Nature gives many other carotenoids, but astaxanthin stands head and shoulders above the rest because of its powerful free radical scavenging activity. Not only that, it safeguards your organs and body cells from the dangerous oxidative damage we’re all prone to.
In addition, this super nutrient reduces DNA damage and is a natural anti-inflammatory. And when it comes to the health of your eyes, astaxanthin delivers particularly strong benefits because it’s able to cross the blood brain barrier AND the blood retinal barrier.
Like many people you may have been told as a child you need to eat plenty of carrots because they’re good for your eyes. This is true because carrots could do contain carotenoids, including vitamin A, which is crucial for the health of your retina. As a matter of fact, if you didn’t have vitamin A you go blind. Luckily, vitamin A is easy to get from the food you eat. Getting plenty of astaxanthin, however, isn’t so easy.
Eye fatigue is known as asthenopia. The symptoms are eye weakness, sensitivity to glare, irritated eyes and poor depth perception. A study in Japan revealed astaxanthin is extremely effective in relieving these symptoms.
Researchers found a 54% reduction in eye fatigue in people who work with computers after taking 6 mg of it a day for four weeks. The studies also suggested it does a better job of preventing eye fatigue than in treating it once it sets in. That’s why early supplementing with this nutrient is important.
There are other eye health benefits as well. It’s associated with lower incidence of cataracts and macular degeneration. But it does much more than promote healthy eyes. The scope of this super nutrient is pretty remarkable.
Other ways astaxanthin can positively impact your health:
The latest research suggests there may be no other singular natural ingredient that can deliver so many beneficial biochemical functions. Astaxanthin can:
If you’d like to find a solution for your eyestrain, you certainly may want to consider giving astaxanthin a try. Even if you aren’t currently having any problems with your eyes the impressive range of health benefits make it one super nutrient you won’t want to do without. You can find the purest form of astaxanthin here.

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]