Unveiling the Hidden Dangers of Oats: What You Need to Know
June 16, 2024
 2234
2234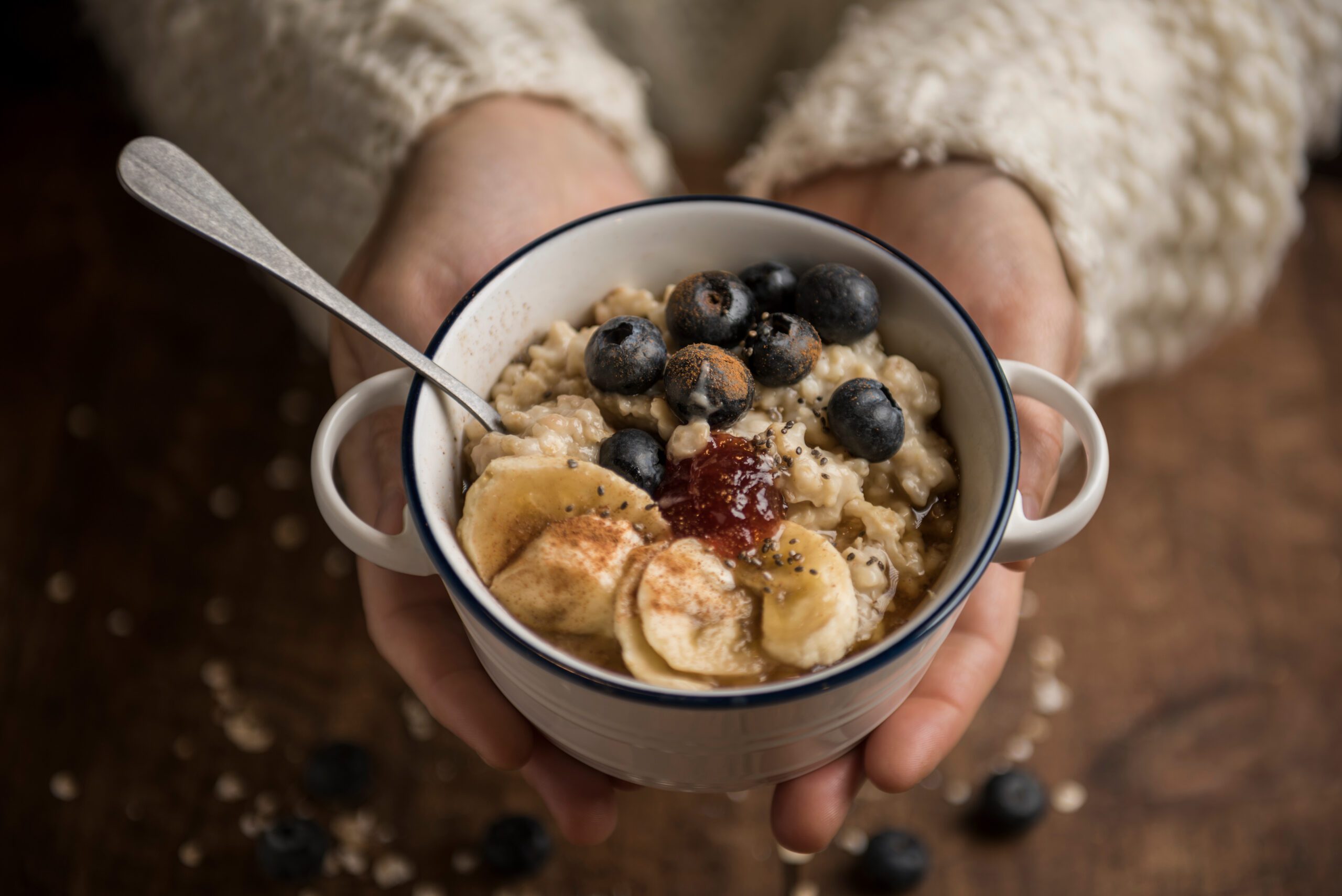 
Oats are scientifically known as Avena sativa….a type of cereal grain primarily grown for their edible seeds, which are commonly consumed by humans and used as livestock feed. Although, there are numerous benefits to eating oats that outweigh the potential downsides, it is important to practice portion control for a healthy diet and fitness routine. Let’s look at the 5 main benefits of eating oats first:
Beta-glucan, a soluble fiber in oats, effectively lowers LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and total cholesterol levels.
The beta-glucan fiber in oats can help improve insulin sensitivity and delay the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream which is beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes.
The soluble fiber in oats can increase feelings of fullness and satiety, which may aid in weight management.
The insoluble fiber in oats can increase stool bulk and promote regular bowel movements.
Oats are a good source of various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, including manganese, phosphorus, magnesium, copper, iron, zinc, folate, and vitamin B1.
The potential downsides of eating oats are possible digestive issues, blood sugar spikes, and gluten contamination. Eating oats is generally not considered bad for you, but there are a few potential downsides to be aware of:
High fiber content can cause digestive issues
especially for those with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or other gastrointestinal issues.
Oats can cause blood sugar spikes because they are rich in carbs, especially if you consume them in large portions or with added sugar. This can be a concern for people trying to manage their blood sugar levels.
While oats are naturally gluten-free, they can become contaminated with gluten during processing or transportation. People with celiac disease or gluten intolerance should search for certified gluten-free oats in ordcer to avoid potential health issues.
Plain, unsweetened oats are relatively healthy. Be sure to read the labels carefully as some of the many flavored oatmeal packets contain brown sugar, honey, and cream that adds significant amounts of sugar, saturated fat, and calories.
For most people, the potential benefits of eating oats, such as their fiber, protein, and nutrient content outweigh the potential downside.
Eat oats in moderation and choose plain, unsweetened oats with healthy toppings to help minimize any negative effects.
If people are unfortunate to experience any of the negative side effects then look for gluten-free and allergy-friendly substitutes that can still be part of a healthy diet foods. Here are some of the best alternatives:
Quinoa is a highly nutritious pseudo-grain rich in protein, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals. It can be cooked similarly to oats and used in recipes such as porridge, granola, or baked goods.
Rice flakes, also known as flattened rice, are a gluten-free alternative to oats. and have a mild flavor that can be used in recipes like porridge, breakfast bars, or crispy treats.
Millet is a gluten-free ancient grain that has a nutty flavor with a light texture . It is high in protein, fiber, and various nutrients, making it suitable for dishes like porridge, grits, pilafs, salads, or baked goods.
It is not a type of wheat and is naturally gluten-free with na nutty flavor. Buckwheat groats can be cooked and used in recipes similar to oats. It has a nutty flavor and is high in B vitamins, fiber, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc.
Chia seeds are rich in fiber, calcium, protein, and antioxidants and can be added to smoothies or mixed with yogurt. It can also be one of the best healthy foods to eat, useful for replacing bread crumbs in meatballs and burgers.
Flaxseed meal is high in protein and fiber and can be used as a substitute for oats in various recipes.
Amaranth is another gluten-free pseudo-grain that is high in protein, calcium, iron, and fiber. Try toasting it before cooking to bring out its nutty flavor and use it as a creamy hot breakfast cereal.
Choosing certified gluten-free oats or using the alternatives described above offers numerous health benefits that outweigh the potential drawbacks.
References:
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/foods/oats
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4325078/
https://foodrevolution.org/blog/oats/
https://www.eatthis.com/reason-shouldnt-eat-oatmeal/
https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-814/oats
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/9-benefits-oats-oatmeal
https://naturesplus.com/blogs/recipes/alternatives-to-oatmeal

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]