What is the endocannabinoid system in the human body and how it works.
March 19, 2023
 717
717 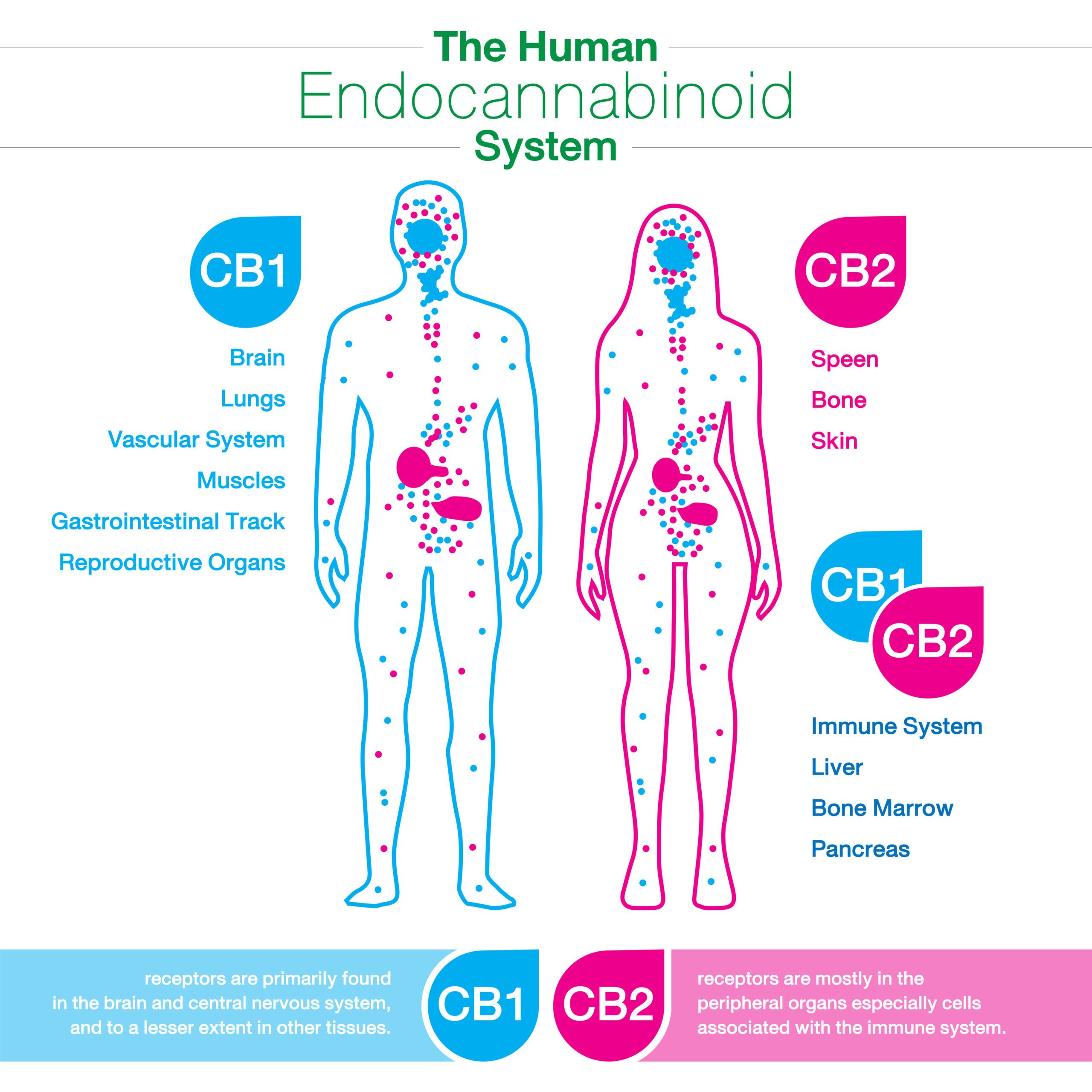
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex signaling system that exists in the human body and other animals. The ECS is made up of three main components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.
Endocannabinoids are molecules that are produced naturally by the body. The two main endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). These molecules are similar in structure to the cannabinoids found in cannabis, such as THC and CBD.
The receptors of the ECS are found throughout the body and are known as CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are primarily located in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are mainly found in immune cells and peripheral tissues.
The enzymes of the ECS are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they have fulfilled their function. The two main enzymes are fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which breaks down anandamide, and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), which breaks down 2-AG.
The ECS plays a role in regulating a variety of physiological processes in the body, including mood, appetite, pain sensation, and immune function. When endocannabinoids bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors, they can activate a variety of signaling pathways that affect these processes.
For example, when anandamide binds to CB1 receptors in the brain, it can produce a feeling of euphoria and relaxation. Similarly, when 2-AG binds to CB2 receptors in immune cells, it can help regulate inflammation.
The ECS is also involved in the effects of cannabis, as the cannabinoids in the plant can bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors in a similar way to endocannabinoids. This is why cannabis can produce a variety of effects on mood, appetite, and pain perception.
Overall, the endocannabinoid system is a complex and important system in the human body that helps regulate a variety of physiological processes.

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]